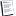
Lavochkin La-174TK 1948
Whereas sweptback surfaces had been adopted for both the La-168 and La-172, the La-174TK, designed to meet the demands of the same specification as the latter, featured unswept surfaces. The wing possessed a thickness ratio of only 6% (the "TK" suffix indicating Tonkoye Krylo, or Thin Wing) which the Lavochkin bureau believed might offer most of the advantages of a thicker sweptback wing while avoiding some of its disadvantages. The basic configuration of the La-174TK reverted to that of the earlier La-152 series fighters, although the relationship was confined to a common design origin, with the single 1590kg NII-1 (RD-500) turbojet exhausting under the rear fuselage. Armament comprised three 23mm NS-23 cannon and flight testing commenced early 1948. Although lighter than the La-172, the La-174TK demonstrated inferior handling and performance characteristics, further development being discontinued. The design bureau designation was reassigned to the replacement prototype for the La-172 which became the La-174D.
Specification
WEIGHTS
Take-off weight 3315 kg 7308 lb
Empty weight 2310 kg 5093 lb
DIMENSIONS
Wingspan 8.64 m 28 ft 4 in
Length 9.41 m 30 ft 10 in
Wing area 13.52 m2 145.53 sq ft
PERFORMANCE
Max. speed 970 km/h 603 mph
Range 960 km 597 miles
Lavochkin La-176 1948
Combining a fuselage essentially similar to that of the Lavochkin La-168 with wings sweptback 45° at quarter-chord, the La-176 was flown in September 1948 with a 2270kg RD-45F turbojet, and armament comprising one 37mm N-37 and two 23mm NS-23 cannon. Re-engined with a Klimov VK-1 turbojet of 2700kg, the La-176 was claimed to have exceeded Mach=1.0 in a dive from 9050m to 6000m on 26 December 1948. It was initially believed that an ASI error had been involved, but the process was repeated six times during January 1949, 1105km/h being recorded at 7500m, this being equivalent to Mach=1.02. The La-176 thus became the first Soviet aircraft to achieve supersonic flight. Further development was abandoned shortly afterwards when the canopy locks failed at high speed, resulting in test pilot Î V Sokolovsky losing his life.
Specification
WEIGHTS
Take-off weight 4631 kg 10210 lb
Empty weight 3111 kg 6859 lb
DIMENSIONS
Wingspan 8.59 m 28 ft 2 in
Length 10.97 m 35 ft 12 in
Wing area 18.25 m2 196.44 sq ft
PERFORMANCE
Max. speed 1043 km/h 648 mph
Range 1000 km 621 miles
Lavochkin La-200 1949
Designed to meet a requirement formulated in 1948 for a two-seat twin-engined all-weather interceptor, the La-200 was flown for the first time on 9 September 1949. Two prototypes were built, each powered by two 2700kg Klimov VK-1 turbojets mounted in tandem with the exhaust of the foremost engine ducted beneath the fuselage. The prototypes differed one from the other primarily in the location of the Torii (Thorium) AI radar, the first prototype having a conical intake centrebody and the second prototype having a radome underslung on the upper intake lip. Armament consisted of three 37mm N-37 cannon, one to port and two to starboard. The wing, sweptback 40° at the leading edge, was largely occupied by integral tankage and two large underwing slipper-type auxiliary tanks could boost maximum range from 1165 to 2000km.
The first prototype was flown on 9 September 1949, and the first and second flight test phases were completed by February and October 1950 respectively, Mach=0.946 being attained in level flight and Mach=1.01 in a dive. The second prototype joined the flight programme early 1951, the repositioned radar being of the improved Torii-A type, ammunition capacity being increased, a ventral keel being introduced and normal loaded weight rising to 10580kg. With the final NII VVS test phase completed in April 1951, a recommendation was made that series production of the La-200 should be initiated. This was thwarted, however, by the issue of a replacement specification in November 1951 calling for a substantial increase in range to permit all-weather standing patrols, and for the provision of heavier, longer-ranging radar. Further work on the La-200 was therefore discontinued in favour of the revised La-200B.
Specification
MODEL La-200 (1st prototype)
WEIGHTS
Take-off weight 10375 kg 22873 lb
Empty weight 7090 kg 15631 lb
DIMENSIONS
Wingspan 12.92 m 42 ft 5 in
Length 16.59 m 54 ft 5 in
Wing area 40.18 m2 432.49 sq ft
PERFORMANCE
Max. speed 1090 km/h 677 mph
Range 1165 km 724 miles

|