Quote:
Originally Posted by CaptainDoggles
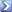
Kurfurst,
Could you kindly post a link to this article written by the australian author directly? I have been waiting almost 2 weeks for my account at allaboutwarfare.com to be activated but it hasn't happened yet.
|
I can re-post for you the original post(s) from July 2004. Needless to say, Neil Stirling got a heart attack when he saw it.

Neil, like some other here were pushing for a pet theory about 100% 100 octane use in FC for some years, but have found no evidence during 10 years of research. It must have been very sobering to him.
Quote:
|
Originally Posted by PipsPriller on Jul 12 2004 at [url
http://www.allaboutwarfare.com/forums/index.php?showtopic=230&st=0&start=0][/url]
The first bulk shipment of 100 octane fuel had arrived in Britain in June 1939 from the Esso refinery in Aruba. This and subsequent tanker shipments from Aruba, Curacao and the USA were stockpiled while the RAF continued to operate on 87 octane petrol. Having secured what were considered reasonably sufficient quantities of 100 octane, Fighter Command began converting its engines to this standard in March 1940, allowing boost (manifold) pressures to be raised without the risk of detonation in the cylinders. This initial increase in maximum boost from 6 lb to 9 lb delivered a useful power growth of around 130hp at the rated altitude.
By the time of the invasion of the Low Countries by Germany in May 1940 the RAF had converted approximately 25 % of it's total fighter force to 100 octane fuel use. The subsequent escalation in air activity and demands placed upon Fighter Command over the next two months put great strain on both the 100 octane fuel stockpiles and aircraft modified to use the fuel. Against the backdrop of total war the RAF found that it's reserves of 100 octane fuel was well below the level considered necessary for widespread use, for any sustained length of time.
Two actions were immediately undertaken by the British War Cabinet in May to resolve the looming crisis. Firstly 87 octane fuel was deemed the primary fuel source to be used until further supplies could be discovered and delivered in sufficient quantities to allow the Merlin conversions to again take place. Those existing fighters already so converted (approximately 125) would continue to use what supplies of 100 octane were available, but all other fighters that had not been modified to continue with the use of 87 octane (of which there was more than adequate supply). The second action was for the British Government to contract the Shell Oil Refining Company to assist the British-controlled Iraqi Petroleum Company at Kirkuk to produce 100 octane fuel. This arrangement proved quite successful as production was quickly converted to 100 octane fuel.
The first Middle East shipment of 100 octane fuel arrived in Portsmouth on 12th August, with a further two deliveries in September and four in October. Although too late to allow widespread conversion for the use of the fuel the deliveries did ensure that from this point on Britain would not be lacking in 100 octane fuel levels. With the newfound supply RAF Fighter Command again embarked upon a Merlin II and III conversion to 100 octane use from late September, finally achieving 100% conversion of it's fighter force by the end of November in 1940.
Given that large quantities were not available until late August, the volume of usage/week of 87 Octane must be far higher than that quoted for 100 Octane.
I came across it when I was in fact researching another subject (Dutch East Indies Fuel levels prior to the Japanese Invasion) at the Australian War Memorial Archives.
It's from a document, copied to the Australian Military Commission in England in February 1941, by Roll Royce to Lord Beaverbrook outlining past, current and proposed changes to the Merlin; and factors that affect it's performance.
It was quite an interesting paper actually, even though i found it to be a very dry subject.
|
The most interesting part is that "Pips" found this well before, in 2004 or earlier, and it agrees with every single document Neil managed to dig up afterwards, though Neil and now Glider tries to discredit this research with whatever means, basically calling Pips a liar behind his back at every opportunity, but never to his face.. The problem is, if Pip would have made it up, he was extremely talented, because Pips information from 2004 - for example that the large scale fighter conversion begun in late September 1940 - agrees perfectly with what Neil found in British archives in 2009 about 87 vs 100 octane consumption rates (and then waited two years before publishing it, as it was obviously not very helpful to his own thesis).
Note that as per the consumption figures, 100 octane did not become the main fuel until late September 1940, just like Pips stated, 7 years ago.